Version control integration¶
Note
Currently only integration with git and mercurial is supported out of the box.
Integration with other version control software should be possible if the version control software allows for external drivers and/or tools. For integration, follow the same patterns as outlined in the manual registration sections.
Git integration¶
Git integration of nbdime is supported in two ways:
through drivers for diff and merge operations, where nbdime takes on the responsibility for performing the diff/merge:
through defining nbdime as diff and merge tools, which allow nbdime to display the diff/merge to the user without having to actually depend on git:
Configure git integration by editing the .gitconfig
(or .git/config) and .gitattributes in each
git repository or in the home/etc directory for global effect.
Details for how to individually configure the different
drivers/tools are given below.
To configure all diff/merge drivers and tools, simply call:
nbdime config-git (--enable | --disable) [--global | --system]
This command will register nbdime with git for the current project
(repository), or on the global (user), or sytem level according to
the --global or --system options.
New in version 0.3: nbdime config-git. Prior to 0.3, each nbdime entrypoint had to enable git integration separately.
Note
When neither the global or system flag is given, the configuration is only applied to the current project (repository). The command will therefore need to be run from within a git repository.
Usage¶
Once configured, the diff/merge drivers should simply work out of the box. For example, the normal git diff command:
git diff [<commit> [<commit>]] [--] [<path>…]
should give you the standard diff for any non-notebook files, but
use nbdime’s command-line diff for all .ipynb files. Nbdime
will also be used for all merges on notebook files (no specific
commands needed).
To launch the rich, web-based tools (for diff visualization and merge conflict visualization/resolution), the following commands will need to be executed:
nbdiff-web [<commit> [<commit>]] [<path>]
See the git diff documentation for further explanation of “<commit>” and “<path>” for this command.
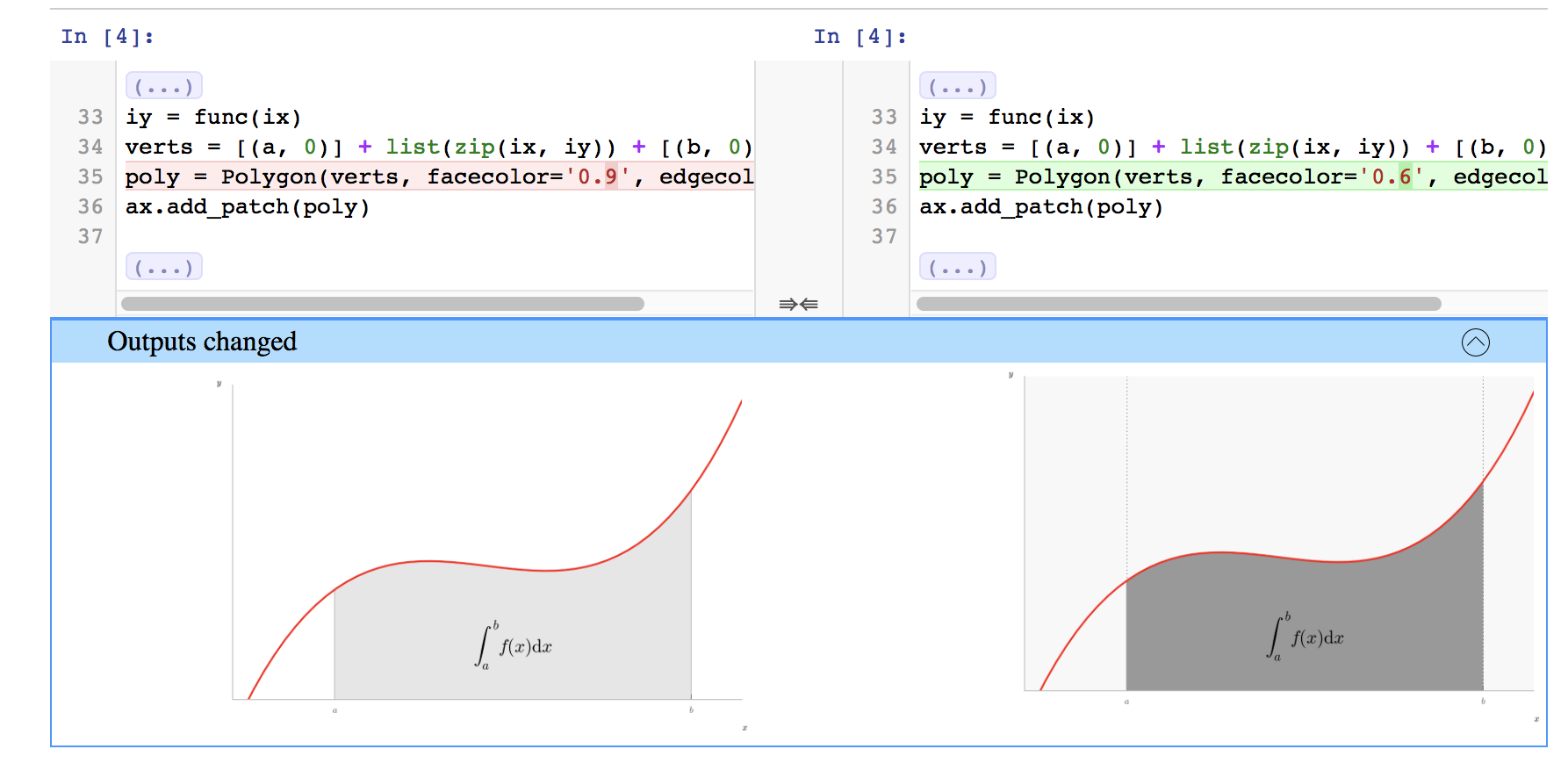
Figure: nbdime’s content-aware diff¶
and:
git mergetool --tool nbdime -- *.ipynb
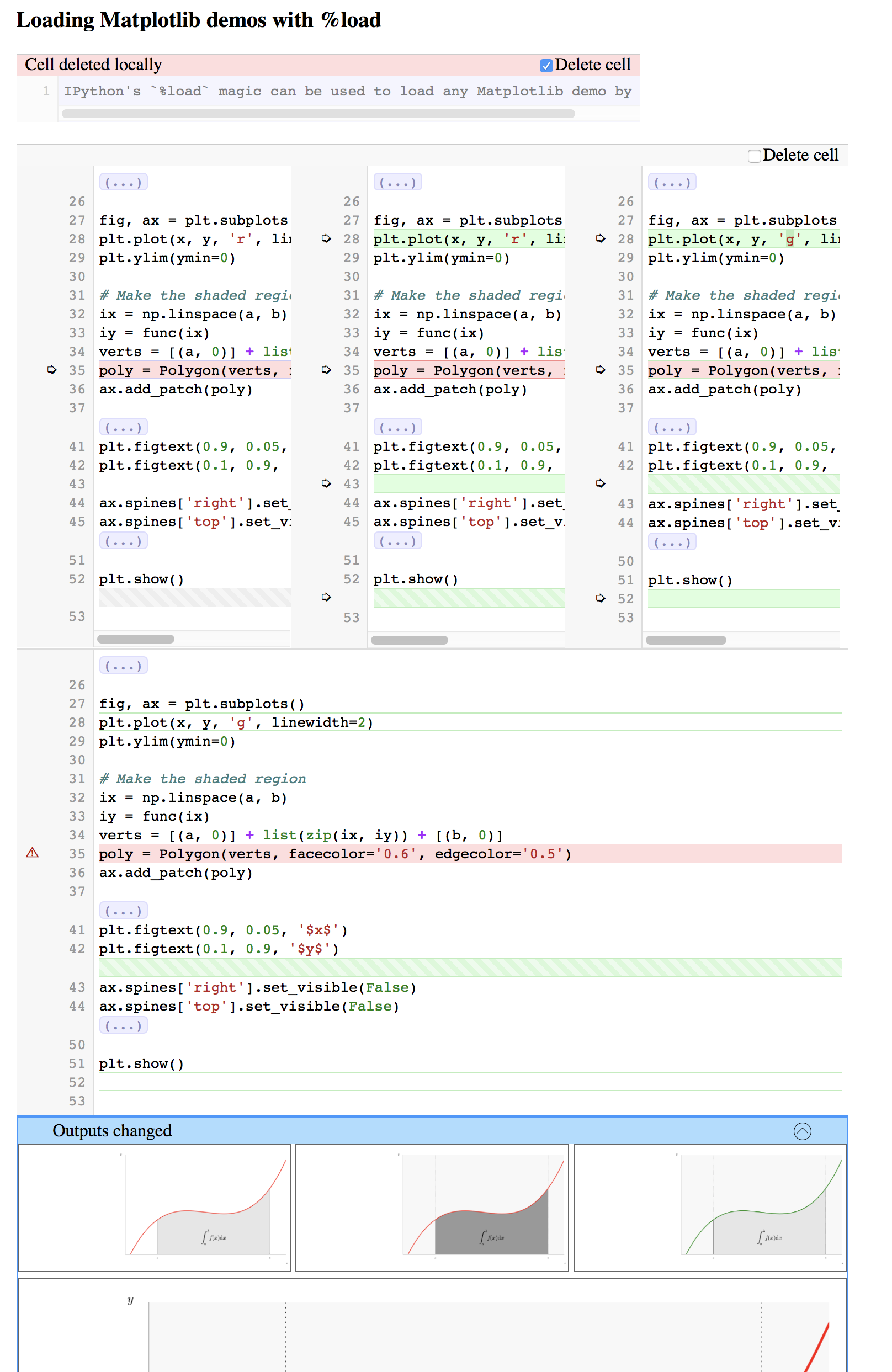
Figure: nbdime’s merge with web-based GUI viewer¶
Note
Using git-nbdiffdriver config overrides the ability to call git difftool with notebooks. Instead, call nbdiff-web in the same way that you call git diff, e.g. git diff [<commit> [<commit>]] [path].
Note
If you simply call git mergetool --tool nbdime, it will be called for all merge conflicts, even on filetypes that it cannot handle. To only call on notebooks, add a filter on file paths, e.g. git mergetool --tool nbdime -- *.ipynb. This command has also been aliased as nbdime mergetool for easy access, and you can also add your own git alias for this command.
Diff driver¶
Registering an external diff driver with git tells git to call that application to calculate and display diffs to the user. The driver will be called for commands such as git diff, but will not be used for all git commands (e.g. git add --patch will not use the driver). Consult the git documentation for further details.
Registration can be done in two ways – at the command line or manually.
Command line registration¶
nbdime supplies an entry point for registering its driver with git:
git-nbdiffdriver config --enable [--global | --system]
This command will register the nbdime diff driver with
git, and associate the diff driver with the .ipynb
file extension. The --global | --system flags work as
explained above.
Manual registration¶
Alternatively, the diff driver can be registered manually with the following steps:
To register the driver with git under the name
"jupyternotebook", add the following entries to the appropriate.gitconfigfile (git config [--global | --system] -e to edit):[diff "jupyternotebook"] command = git-nbdiffdriver diff
or if you prefer to use webdiff:
[diff "jupyternotebook"] command = git-nbdiffdriver webdiff [--ip IP]
To associate the diff driver with a file type, add the following entry to the appropriate
.gitattributesfile:*.ipynb diff=jupyternotebook
Merge driver¶
Registering an external merge driver with git tells git to call that driver application to calculate merges of certain files. This allows nbdime to become responsible for merging all notebooks.
Registration can be done in two ways – at the command line or manually.
Command line registration¶
nbdime supplies an entry point for registering its merge driver with git:
git-nbmergedriver config --enable [--global | --system]
This command will register the nbdime merge driver with
git, and associate the merge driver with the .ipynb
file extension. The --global | --system flags work as
explained above.
Manual registration¶
Alternatively, the merge driver can be registered manually with the following steps:
To register the driver with git under the name “jupyternotebook”, add the following entries to the appropriate
.gitconfigfile (git config [--global | --system] -e to edit):[merge "jupyternotebook"] command = git-nbmergedriver merge %O %A %B %L %P
To associate the merge driver with a file type, add the following entry to the appropriate
.gitattributesfile:*.ipynb merge=jupyternotebook
Merge web tool¶
The rich, web-based merge view can be installed as a git merge tool. This enables nbdime to process merge conflicts during merging in git, and present them for resolution.
Command line registration¶
To register nbdime as a git merge tool, run the command:
git-nbmergetool config --enable [--global | --system]
Once registered, the merge tool can be started by running the git command:
git mergetool --tool=nbdime [<file>…]
If you want to avoid specifying the tool each time, nbdime
can be set as the default tool by adding the --set-default
flag to the registration command:
git-nbmergetool config --enable --set-default [--global | --system]
This will allow the merge tool to be launched simply by:
git mergetool [<file>…]
Note
Git does not allow to select different tools per file type, so if you set nbdime as the default tool it will be called for all merge conflicts. This includes non-notebooks, which nbdime will fail to process. For most repositories, it will therefore not make sense to have nbdime as the default, but rather to call it selectively.
Manual registration¶
Alternatively, the merge tool can be registered manually with the following steps:
To register both the merge tool with git under the name “nbdime”, add the following entry to the appropriate
.gitconfigfile (git config [--global | --system] -e to edit):[mergetool "nbdime"] cmd = git-nbmergetool "$BASE" "$LOCAL" "$REMOTE" "$MERGED"
To set nbdime as the default merge tool, add or modify the following entry in the appropriate
.gitconfigfile:[merge] tool = nbdime
Mercurial integration¶
Integration of mercurial is similar to that for manual git registration, but it uses a separate set of entry points since amongst others, mercurial requires the diff extension to handle directories.
Differs¶
To tell mercurial about nbdimes differs, open the appropriate config file (hg config --edit for the default user level one), and add the following entries:
[extensions]
extdiff =
[extdiff]
cmd.nbdiff = hg-nbdiff
cmd.nbdiffweb = hg-nbdiffweb
opts.nbdiffweb = --log-level ERROR
- This will:
enable the external diff extension
register both the command line diff and web diff
set the default log level of the webdiff
opts.<cmdname> allows you to customize which
flags nbdime are called with.
To use nbdime from mercurial, you can then call it like this:
hg nbdiff <same arguments as for 'hg diff'>
hg nbdiffweb <same arguments as for 'hg diff'>
Mergetools¶
Add the following entries to the appropriate mercurial config file:
[merge-tools]
nbdime.priority = 2
nbdime.premerge = False
nbdime.executable = hg-nbmerge
nbdime.args = $base $local $other $output
nbdimeweb.priority = 1
nbdimeweb.premerge = False
nbdimeweb.executable = hg-nbmergeweb
nbdimeweb.args = --log-level ERROR $base $local $other $output
nbdimeweb.gui = True
[merge-patterns]
**.ipynb = nbdime
- This will:
use the merge driver by default for notebook files
register the web tool
The typical usage pattern for the webtool is like this:
> hg merge <other branch>
merging ***.ipynb
0 files updated, 0 files merged, 0 files removed, 1 files unresolved
use 'hg resolve' to retry unresolved file merges or 'hg update -C .' to abandon
> hg resolve --tool nbdimeweb